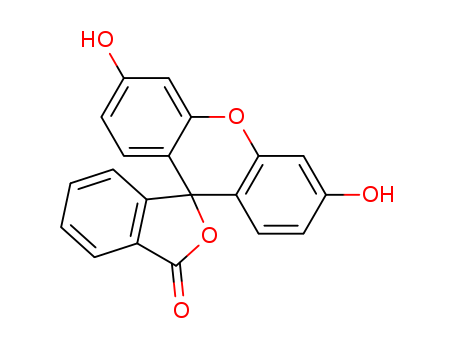
Fluorescein
- CAS No. :2321-07-5
- Molecular Formula:C<sub>20</sub>H<sub>12</sub>O<sub>5</sub>
- Purity:
- Molecular Weight:332.312
Product Details
pd_meltingpoint:314-316 °C
Appearance:orange-red crystalline powder
Offer Chemical Raw Material Fluorescein 2321-07-5 In Stock
- Molecular Formula:C20H12O5
- Molecular Weight:332.312
- Appearance/Colour:orange-red crystalline powder
- Melting Point:314-316 °C
- Refractive Index:1.5000 (estimate)
- Boiling Point:620.8 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:2.2, 4.4, 6.7(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:232.6 °C
- PSA:87.74000
- Density:1.602 g/cm3
- LogP:3.96860
Fluorescein(Cas 2321-07-5) Usage
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Fluorescein is incompatible with strong oxidizers. Also incompatible with acids, acid salts and salts of heavy metals. . |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Fluorescein is not available, but Fluorescein is probably combustible. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also FLUORESCEIN SODIUM. |
|
Safety |
Topical, oral, and intravenous use of fluorescein can cause adverse reactions, including nausea, vomiting, hives, acute hypotension, anaphylaxis and related anaphylactoid reaction, causing cardiac arrest and sudden death due to anaphylactic shock. The most common adverse reaction is nausea, due to a difference in the pH from the body and the pH of the sodium fluorescein dye; a number of other factors , however, are considered contributors as well. The nausea usually is transient and subsides quickly. Hives can range from a minor annoyance to severe, and a single dose of antihistamine may give complete relief. Anaphylactic shock and subsequent cardiac arrest and sudden death are very rare, but because they occur within minutes, a health care provider who uses fluorescein should be prepared to perform emergency resuscitation. |
|
Synthesis |
Fluorescein was first synthesized by Adolf von Baeyer in 1871. It can be prepared from phthalic anhydride and resorcinol in the presence of zinc chloride via the Friedel - Crafts reaction. A second method to prepare fluorescein uses methanesulfonic acid as a Br?nsted acid catalyst. This route has a high yield under milder conditions. |
|
Derivatives |
There are many fluorescein derivatives. For example, fluorescein isothiocyanate 1, often abbreviated as FITC, is the original fluorescein molecule functionalized with an isothiocyanate group ( - N = C = S ) , replacing a hydrogen atom on the bottom ring of the structure. This derivative is reactive towards primary amine groups of biologically relevant compounds including intracellular proteins to form a thiourea linkage. A succinimidyl ester functional group attached to the fluorescein core, creating NHS-fluorescein, forms another common amine-reactive derivative, yielding more stable amide adducts. Penta fluoro phenyl esters (PFP) and tetra fluoro phenyl esters (TFP) are other useful reagents. In oligonucleotide synthesis, several phosphoramidite reagents containing protected fluorescein, e.g. 6-FAM phosphoramidite 2, are widely used for the preparation of fluorescein-labeled oligonucleotides. Other green dyes include Oregon Green, Tokyo Green, SNAFL, and carboxy naphtho fluorescein. These dyes, along with newer fluoro phores such as Alexa 488, Fluo Probes 488 and DyLight 488, have been tailored for various chemical and biological applications where higher photo stability, different spectral characteristics, or different attachment groups are needed. |
|
Physical properties |
The fluorescence of this molecule is very intense; peak excitation occurs at 494 nm and peak emission at 521 nm. Fluorescein has a pKa of 6.4, and its ionization equilibrium leads to pH-dependent absorption and emission over the range of 5 to 9. Also, the fluorescence lifetimes of the protonated and deprotonated forms of fluorescein are approximately 3 and 4 ns, which allows for pH determination from non intensity based measurements. The lifetimes can be recovered using time-correlated single photon counting or phase-modulation fluorimetry. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A xanthene dye that is highly fluorescent, detectable even when present in minute quantities. Used forensically to detect traces of blood, in analytical chemistry as an indicator in silver nitrate titrations and in microscopy. |
|
Application |
Biochemical research In cellular biology, the isothiocyanate derivative of fluorescein is often used to label and track cells in fluorescence microscopy applications (for example, flow cytometry). Additional biologically active molecules (such as antibodies) may also be attached to fluorescein, allowing biologists to target the fluorophore to specific proteins or structures within cells. This application is common in yeast display. Health care applications "Fluorescein sodium", the sodium salt of fluorescein, is used extensively as a diagnostic tool in the field of ophthalmology and optometry, where topical fluorescein is used in the diagnosis of corneal abrasions, corneal ulcers and herpetic corneal infections. It is also used in rigid gas permeable contact lens fitting to evaluate the tear layer under the lens. Uses in river systems In 1966, environmentalists forced a change to a vegetable-based dye to protect local wildlife. Other uses of fluorescein include using it as a water-soluble dye added to rainwater in environmental testing simulations to aid in locating and analyzing any water leaks, and in Australia and New Zealand as a methylated spirit dye. Oil field application Fluorescein dye solutions, typically 15 % active, are commonly used as an aid to leak detection during hydrostatic testing of sub sea oil and gas pipelines and other subsea infrastructure. Leaks can be detected by divers carrying ultraviolet lights. |
|
General Description |
Yellow amorphous solid or orange-red crystals. Latter have greenish-yellow fluorescence by reflected light. Insoluble in water. Soluble in dilute aqueous bases. Very dilute alkaline solutions exhibit intense, greenish-yellow fluorescence by reflected light. Low toxicity. May be sensitive to prolonged exposure to light. |
InChI:InChI=1/C20H12O5/c21-11-5-7-15-17(9-11)24-18-10-12(22)6-8-16(18)20(15)14-4-2-1-3-13(14)19(23)25-20/h1-10,21-22H
2321-07-5 Relevant articles
DESIGN, SYNTHESIS, AND PHOTOPHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A NOVEL NIR II DYE FOR BIOLOGICAL IMAGING AND OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICES
-
, (2022/03/04)
In one aspect, the disclosure relates to...
Synthesis and evaluation of intrinsic bioactivity of fluorescein and phenolphthalein derivatives
Bharathkumar, Kuruba,Durairaj, Arulappan,Mohanapriya, Raman,Obadiah, Asir,Ramanathan, Subramanian,Santhoshkumar, Palanichamy,Vasanthkumar, Samuel
, (2021/09/28)
Fluorescein and phenolphthalein derivati...
Lipase mimetic cyclodextrins
Lee, Youngjun,Devaraj, Neal K.
, p. 1090 - 1094 (2021/02/06)
Glycerophospholipids (GPLs) perform nume...
Chemistry of the carboxylic acid of dihydrofluorescein in oxidation and its application to fluorogenic ROS sensing
Le, Hoa Thi,Nguyen, Dinh Phi Long,Shin, Hyo Seob,Jung, Woong,Kang, Chulhun,Kim, Tae Woo
, p. 461 - 468 (2021/07/19)
The conjugation site of dihydrofluoresce...
2321-07-5 Process route

-
![3′,6′-dimethoxy-3H-spiro[isobenzofuran-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one](/upload/2024/8/fd0c74b1-41d0-46b1-b278-63c2ce65287d.png)
- 36886-76-7
3′,6′-dimethoxy-3H-spiro[isobenzofuran-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one
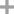
-
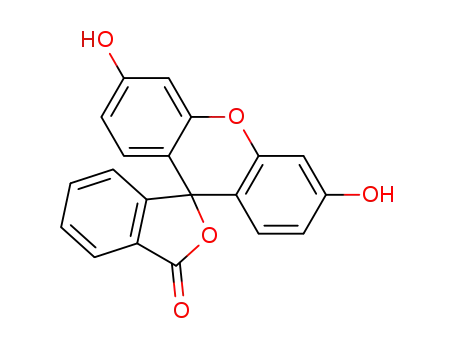
- 2321-07-5,126605-73-0
fluorescein
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogenchloride; acetic acid; at 150 - 160 ℃; unter Druck;
|
-
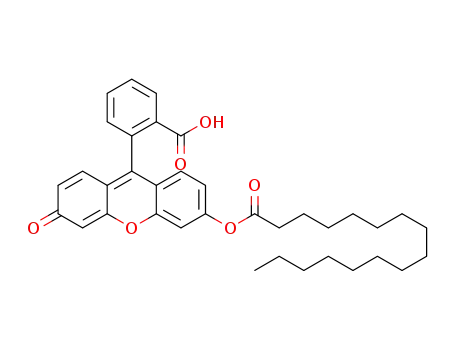
-
C36H42O6

-
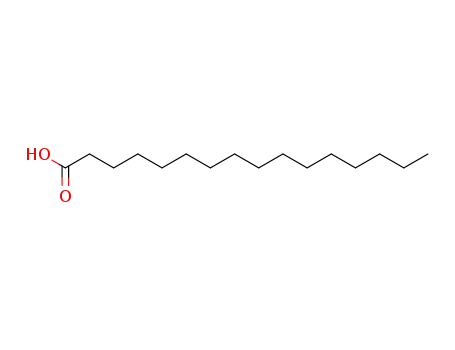
- 57-10-3
1-hexadecylcarboxylic acid

-

- 2321-07-5,126605-73-0
fluorescein
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hexakis[6-deoxy-6-amino]-α-cyclodextrin; water; In dimethyl sulfoxide; at 37 ℃; for 0.5h; pH=8; Reagent/catalyst;
|
2321-07-5 Upstream products
-
85-44-9
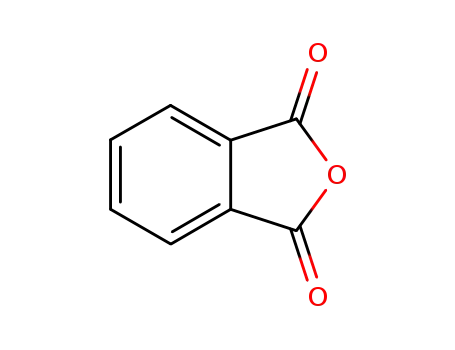
phthalic anhydride
-
89-84-9
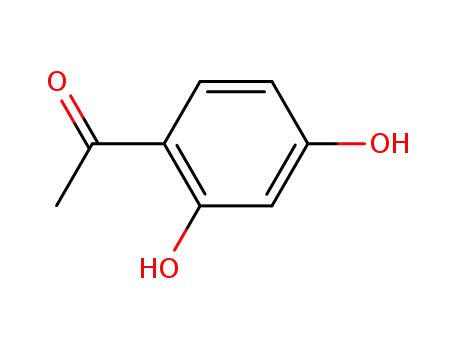
2',4'-dihydroxy-4-acetophenone
-
490-11-9
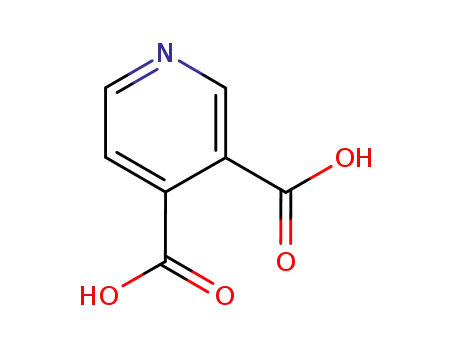
3,4-pyridinecarboxylic acid
-
108-46-3
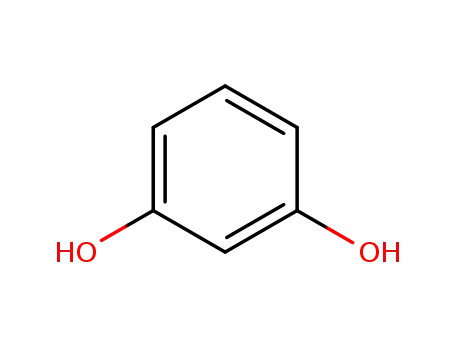
recorcinol
2321-07-5 Downstream products
-
87569-96-8
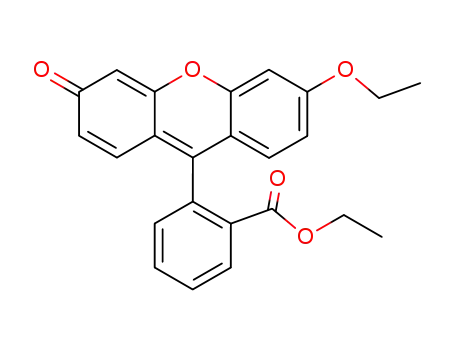
2-(6'-ethoxy-3'-oxo-3'H-xanthene-9'-yl)benzoic acid ethyl ester
-
70672-06-9
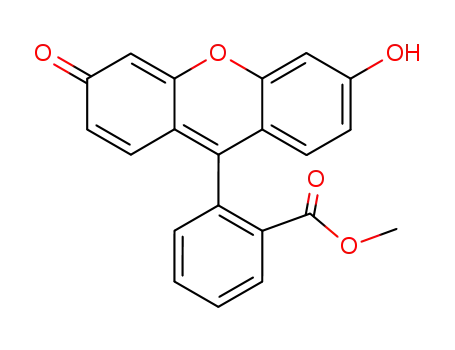
methyl 2-(6-hydroxy-3-oxo-3H-xanthen-9-yl)benzoate
-
72616-76-3
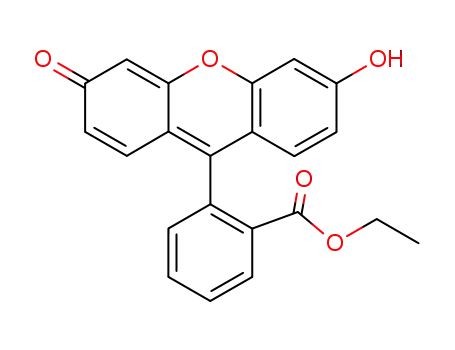
ethyl fluorescein
-
15905-32-5
erythrosine B
Fluorescein, an orange red powder. In biological research, it is a commonly used fluorescent dye used to label biomolecules such as cells, proteins, and nucleic acids for observation and study of their distribution, movement, and interactions under a fluorescence microscope. For example, in immunofluorescence experiments, it is used to label antibodies to detect specific antigens. In the field of analytical chemistry, it can be used as a fluorescent indicator to detect the presence and concentration of certain substances. Fluorescein is usually prepared through specific chemical synthesis methods and plays an important role in fields such as life sciences and chemical analysis.